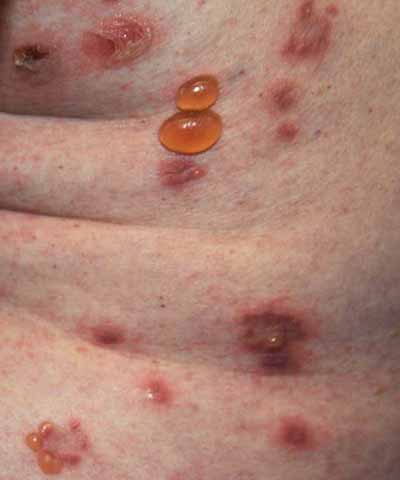
Pemphigoid
Background
- Commonest autoimmune sub-epidermal blistering disorder
- Auto-antibodies vs “adhesion complexes” in skin’s basement membrane = blister
- High relapse rate
Clinical
- Itchy +, tense fluid filled blisters skin ± mucous memb
- Usually limbs, groin, and abdomen
- Older patients
- Beware septicaemia (esp. if immunocompromised)
Differential Dx
- Bullous pemphigoid
- Linear IgA disease
- Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita
- Bullous drug reaction
Investigations
- Clinical diagnosis
- Confirmatory biopsy ± immunofluorescence
- ↑CRP & ↑ESR
Management
- Potent topical steroids (clobetasol propionate)
- Oral steroids or Dapsone (esp. for mucous membrane disease)
- Tetracyclines ± nicotinamide in milder cases
- Immunosuppressants (MTX / Azathioprine) in severe cases
- Regular skin antiseptic soaks. and protective non-adherent dressings
Content by Dr Íomhar O' Sullivan. Last review Dr ÍOS7/01/23.