Background
Information from the Australasian ANZSCTS/ANZICS guidelines on cardiothoracic advanced life support (CALS-ANZ) 2022.
- Most post cardiothoracic surgery arrests occur early
- Many are due to reversible causes e.g. cardiac tamponade/haemorrhage
- The NZSCTS/ANZICS group have published specific resusc. protocols for this group
CALS algorithm
Resternotomy
How to
- Adhesive surgical drape on patient's chest
- Cut skin sutures
- Remove closure wires/plates
- Insert retractor to expose heart
- Remove any clots
- 2 handed internal cardiac massage
- If shockable, internal defib. pads at 20 J
Kit
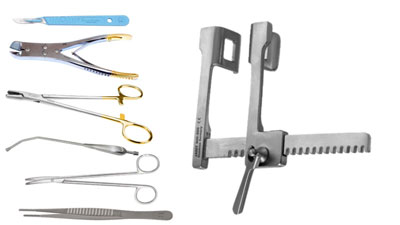
Image thanks to christian.karcher@mh.org.au
Notes
- Shortly post-op, external cardiac massage may be delayed for 60 seconds to help ID/Treat reversible causes:
- Fibrillation
- Pacing
- Pericardial tamponade
- Tension PTX
- Massive haemorrhage
- Immediate resternotomy considered if <10 days post-op
- Avoid XS adrenaline (use 50-100mG IV instead of 1mg)
- Consider Amiodarone (300mg IV) in refractory VF
- If ROSC occurs before commencing a resternotomy, continue preparing for a resternotomy until the patient is stable
- If ROSC occurs during the resternotomy, remove the sternal closing devices and await the cardiothoracic surgeons
Links
- ANZSCTS/ANZICS (CALS-ANZ). DOI:10.51893/2022.3.SA3