Aetiology
Infections
- Coxsackie, bacterial, TB
Neoplastic
Drugs
- Procainamide, Hydralazine
Autoimmune
- Rheumatoid, SLE, Sarcoidosis
Approach
Diagnosis
Acute pericarditis is an inflammatory pericardial syndrome with or without pericardial effusion.
The clinical diagnosis can be made with two of the 4 criteria:
- Pericarditic chest pain (pleuritic, eased by siting up) [90% of cases]
- Pericardial rub [30%]
- New widespread ST-elevation or PR depression [60%]
- Pericardial effusion (new or worsening)[60%]
Inflam. markers may be raised.
CXR usually normal (unless effusion).
TnI may be raise if concomitant myocarditis.
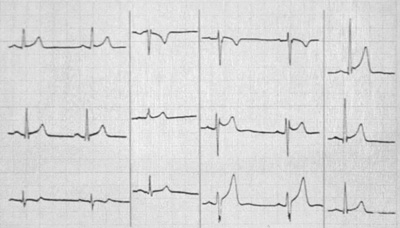
ECG
- Diffuse concave ST elevation (ST depression in V1)
- Low voltage if effusion
- Later flattening or inversion T globally
- Return to normal(3/12)
Treatment
- Aspirin (750-1000mg every 8hrs) plus PPI for 2 weeks
or - Ibuprofen (600mg every 8 hours) plus PPI for 2 weeks
plus - Colchicine 0.5mg once (<70kg) or 0.5mg bd (≥70kg) for up to 3 months
- Refer cardiology if cardiac compromise or recurrent