Urticaria (hives / wheals)
Aetiology
- Viral: e.g. EBV, hepatitis (A,B &C), HSV
- Bacterial: e.g. Streptococcal
- Parasitic
- Insect bites (last longer that 24hrs)
- Drug rxn: Urticarial rash may appear a 14/7 after stopping penicillin
Rash
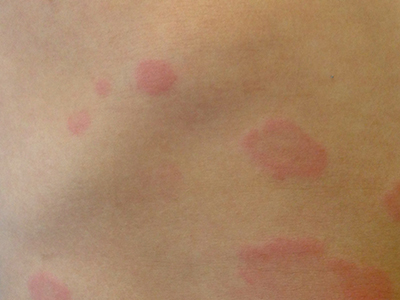 Urticarial wheals. Image from wikimedia.org
Urticarial wheals. Image from wikimedia.org
Clinical
- Itchy++, raised (palpable), blanching (with pressure) wheals
- Rash is transient (hours) and moves location/shape
- Dermatographism — urticarial lesions with light scratching
- No permanent scarring / pigmentation (cf "beware")
- Many have oedema of eyelids, perioral and feet / extremities
Beware
- Angioedema of the lips: suggests autoimmune aetiology:
- Ecchymosis/pigmentated lesions: suggest vasculitis
- Systemic signs of wt loss, arthralgia, lymphadenopathy
- Any signs jaundice (cholestatic itch)?
- SIRS or other indicators of sepsis?
DDx (itch)
- Erythema multiforme
- Contact dermatitis (slower onset and offset)
- Atopic dermatitis
- Insect bites (fixed location)
- Drug reaction
Management
- Avoidance of trigger
- H1-receptor blockers:
- Loratadine or cetirizine (non-sedating)
- Chlorphenamine or promethazine only if sedation needed (itch insomnia)
- Education re anaphylaxis (± adrenaline prescription)
Content by Dr Íomhar O' Sullivan. Last review Dr ÍOS 15/04/24.
