Eyes must always be inspected particularly if there is a wound of the overlying lid or the lids are swollen. If they cannot be retracted, consider requesting senior help directly or reviewing the patient the next morning (- at the latest). Visual acuity must be checked. Failure to do this could lead to the loss of a patient's eye.
Foreign Bodies
The most common eye condition seen in the Emergency Department. Foreign bodies usually lodge either in the upper tarsal plate, conjunctiva or cornea.
Foreign Body from the Upper Tarsal Plate
These are easy to remove. Evert the eyelid with the help of a cotton wool bud and remove the foreign body.
Foreign Body seen on the Cornea
- Instil Benoxinate
- After a minute or so dislodge the foreign body with a cotton bud or failing that, a fine needle (blue or green) and then remove the foreign body with the cotton bud. Make sure there is no rust mark or rust ring. Superficial corneal foreign bodies (easily removed with cotton bud) do not require antibiotic cover [Bestbets]
- Deeper lesions ( e.g. requiring removal with a needle) may be treated with Chloromycetin Ointment Q.I.D. Pad for 4 hours. Review patient the following day. If the rust ring is there, this should be removed with the help of a needle after Benoxinate. If rust ring difficult, refer
Corneal Abrasion
- Usually caused by a child's finger, branches of trees, leaves, sometimes a flying object
- Inspect the eye - instil Benoxinate, a few drops of fluorescein and use blue light to detect the abrasion
- Apply Chloramphenicol eye ointment and repeat 8 hourly
- Eye patch is not necessary in most cases [Bestbets]
- Double pad (and consider topical; NSAIDS [Bestbets]) for 24 hrs if abrasion large or painful
- Patient should be advised to rest on that day and to attend the following day if not resolved
- Corneal abrasions usually heal within 2 days
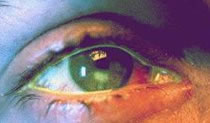
Intra-ocular Foreign Bodies
Hx is very important. Persons working with heavy revolving machinery, chisel and hammer etc. are at risk. A fragment of metallic foreign body can penetrate the cornea and lodge in the vitreous. If you are unable to see any foreign body over the cornea and the patient is having discomfort, photophobia, severe pain and seeing floating objects in the field of vision, suspect F.B. Obtain an x-ray to exclude intra-ocular radio-opaque foreign body. If confirmed patient must be referred to Eye Hospital straight away, x-ray film to accompany.
Other Serious Penetrating Injuries
E.g. collapse of the anterior chamber, laceration to cornea, or iris, hyphaema etc. Very painful eye, detachment of the retina. Patient should be referred to Eye Hospital as soon as possible as a stretcher case. Analgesia should be given for pain and apply eye shield to prevent pressure and extrusion of eye content.
Sub-Conjunctival Haemorrhage
- No special treatment
- Check BP
Stye
- Bathe with salt water
- Chloramphenicol ointment tds
- See GP: Sometimes also give oral antibiotics
Herpes Zoster Opthalmicus
If diagnosis is certain refer patient to Eye Hospital as soon as possible.
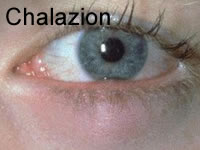
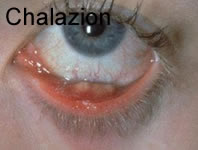
Chalazion (Meibomian Cyst)
- Reassure
- Refer to GP
- GP to refer to Eye Clinic for surgical treatment
Iritis
Painful eye, photophobia, constricted or irregular pupil, headache, nausea. Refer to Eye Hospital. See acute red eye.
Pterygium
Reassure. Refer to GP who can refer to Eye Clinic for surgical treatment.
Acute Glaucoma
Unwell, painful eye, acuity down, haloes, may be vomiting.
Steamy cornea.
Pupil unreactive, fixed or semi-dilated.
Refer to Eye Hospital. See acute red eye.
Retinal Haemorrhage and Detachment
Patient should be transported to Eye Hospital as a stretcher case.
Laceration of Eyelids
Any laceration around the naso-lacrimal duct refer to Eye Hospital. Beware upper lid laceration which penetrates globe.
Arc Flash
Very painful. Photophobic condition.
Chloramphenicol ointment.
Pad for 24 hours.
Analgesic and bed rest. Use cyclopentolate to reduce iris spasm if very painful and photophobic.
May need steroids if cornea very oedematous - discuss with Eye Emergency Department.
Chemical Burns
Instil Benoxinate drops. Irrigate for many minutes. Examine cornea. Refer.
Acid in the Eyes
- Benoxinate 0.5% to relieve pain
- Irrigation, irrigation, irrigation of eye for several minutes with N/Saline eye solution
- Check with litmus paper to ensure complete removal
- Continue treatment as for corneal abrasion
- Discuss with Eye Hospital
Any other Irritants
- Eye irrigation (warmed [33-37°] solution [Evidence])for several minutes and then continue as for corneal abrasion
Paint
- Benoxinate 0.5% for relief of pain
- Clean the surrounding area with liquid paraffin, then Chloramphenicol
- Review after 24 hours
Caustic Soda, Plaster, other Alkalis
- Benoxinate 0.5% for relief of pain
- Irrigate eye for at least 30 minutes with water
- Remove any particles and shield
- Refer to Eye Hospital now
Contact Lenses
Sometimes produce conjunctivitis. Give antibiotic drops e.g. neosporin. Advise to see Optician.
Black Eye
Blow to eye. A Champagne cork or squash ball can cause haemorrhage inside the eye ball or even detachment of the retina. If blow out fracture, refer to Eye Hospital. If no underlying damage, usually settles down within 5-7 days.
Links
Links CUH
- Eye casualty Reg. SIVUH (08:30-20:00) 021 4260903 / 021 4260904
- Unstable patients (can't transfer) call Ophth. Reg on calls 021 4926100
- After 20:00 Eye Reg. via SIVUH switch 021 4926100