Cysticercosis
Background
- Infection with the larval form (or cysticercus) of the pork tapeworm Taenia solium
- Principally Latin America, Asia, and Africa
- Infection to symptoms may take years
- Commonest in CNS = neurocysticercosis
- Seizures, ↑ICP , meningitis, cranial N. palsies
- Otherwise, calcified cysts (cysticerci-encysted larvae) in muscle, skin, eyes, heart
Diagnosis
- Dx by A) Imaging and B) Serology
- CT sensitive for calcification
- MRI sensitive for surrounding oedema
- Most infections are asymptomatic & benign
- Untreated cysticercosis with hydrocephalus or immune reactions may cause cerebral infarction
Management
- Focus on ABCs
- Control seizures, cerebral oedema, hydrocephalus
- Anthelminthic therapy only if live (non-calcified) cysticerci
- Anthelminthic therapy, kills viable cysts and provokes an inflam. response, may ↑ symptoms acutely
- Co-administration of dexamethasone to mitigate inflam. response
- Antihelminthics: Albendazole or Praziquantel
Prevention
- Avoid food that is potentially contaminated by human faeces
- Good food handling practices
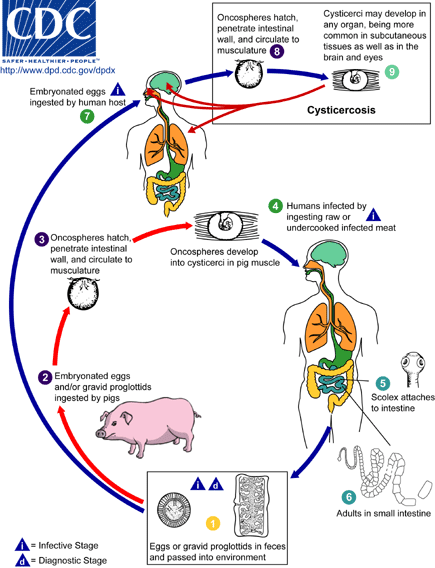 Cysticercosis - From CDC site
Cysticercosis - From CDC site
Content by Dr Íomhar O' Sullivan. Last review Dr ÍOS 16/04/22.

