Hydatid disease - Echinococcosis
Background
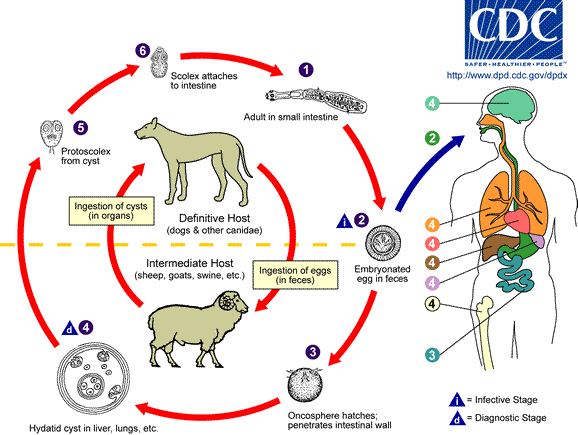 Image with kind permission of the CDC-DPDx team.
Image with kind permission of the CDC-DPDx team.
- Infection caused by the larval stage of small taeniid-type tapeworms of the Echinococcus species
- 3 forms of human hydatid disease
- E granulosus unilocular cyst
- E vogeli unilocular cysts
- E multilocularis multilocular locally invasive
- The adult form of E granulosus (3-5mm long) inhabits the intestines of definitive hosts (e.g. dogs)
- Ingested eggs hatch into embryos which penetrate intestine, portal circulation to liver
- Hydatid cysts in liver (occas. other organs e.g. lungs / brain)
- Each cyst, grows 2 cm/year, has 2 layers
- endocyst = fluid
- pericyst = capsule, new larvae site
Clinical
- Most uncomplicated cysts asymptomatic
- Maybe vague RUQ pain ± liver mass
- Rarely, raised eosinophil count
- Cyst rupture
- Intra-biliary = jaundice, colic, ascending cholangitis
- Intra-peritoneal = severe abdo pain, peritonism
- Allergic reaction common (± anaphylaxis), eosinophilia
- Pulmonary cyst = chest pain, cough, haemoptysis
Investigations
- Plain x-rays for pulmonary masses - heterogeneous appearance
- Ultrasound for hepatic, fluid filled, cysts
- CT for pre-op planning
- Serological immunoelectrophoresis most sensitive for diagnostic and monitoring
- ELISA less specific and may remain positive for months after curative surgery
Treatment
- Surgical cystectomy (aspiration and injection if inoperable) is treatment of choice
- Albendazole / mebendazole for those where surgery contraindicated
Content by Dr Íomhar O' Sullivan. Last review Dr ÍOS 16/04/22.
