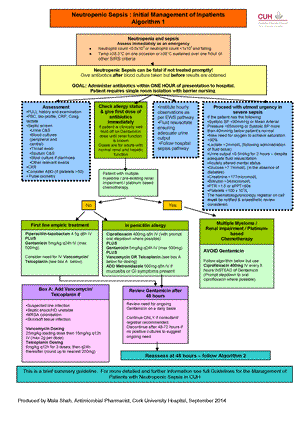
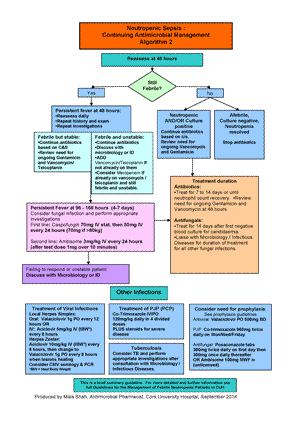
Neutropenic fever
Pyrexia >38° C for over one hour duration or >38.3°C on one occasion in a neutropenic adult:.
- If likely to have protracted (> 5 days) neutropenia, patient should be nursed in a room with HEPA filtered air (Ward 2D in CUH)
Neutropenia
- Defined as neutrophils ≤1
- Functional neutrophilia - following recent chemotherapy even with levels >1
- Myelodysplastic patients have functional neutropenia even with "normal" neutrophil levels
- In general, patients attending haematology OPD monthly, are at risk of neutropenia
Background
- Bacteraemia in 30% (60% of which is Gram Positive - Staphylococcus from lines or Strep in mucositis)
- Most dangerous are Gram negative from patients bowel
- Fungal infections are uncommon and associated with prolonged neutropenia and broad spectrum antibiotics
- Netilmicin no longer available
- 3rd generation cephalosporin use is associated with C difficile and Vancomycin resistant enterococci
Examination
Full clinical examination but note particularly: Pulse, BP, mouth, chest, perineum, line sites, skin, fundi.
Investigations
- FBC, U&E Cr., LFT, CRP, CXR, sinus or dental x rays if symptomatic
- Blood culture - peripheral and central line if present
- Swabs from appropriate inflamed sites
- MSU if symptomatic
- Faeces if diarrhoea and/or if fungal infection suspected, check C. difficile toxin
- Aspergillus precipitans and PCR
- Serology, mouthwash, vesicle fluid for virology if indicated
Management
Please see https://nchd.ie