Clinical
- Sudden onset of fever (pyrexia ≥ 38°C) and cough or sore throat
- Other symptoms can include rhinorrhoea, limb or joint pain, headache, vomiting or diarrhoea
At risk groups
- children <2 years
- Chronic respiratory disease, including asthma
- Chronic heart, kidney, liver or neurological disease
- Immunosuppression (whether caused by disease or treatment)
- Diabetes mellitus
- Haemoglobinopathies
- Children with any condition (e.g. cognitive dysfunction, spinal cord injury, seizure disorder or other NM disorder) that can compromise respiratory function, especially those attending special schools/day centres
- Severely obese people (BMI ≥40)
- People aged 65 years and older
- Pregnant women
Investigations
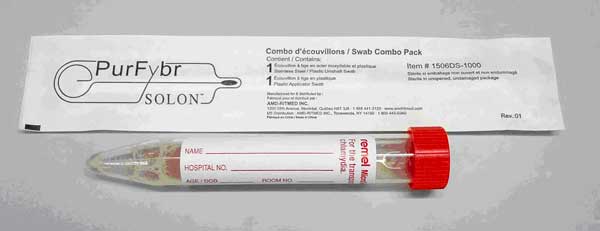
"Clinicians at MUH are now (January 2015) able to test for Influenza in the microbiology laboratory, Mercy University Hospital. This test will be performed using an appropriately labelled nasal swab (Red capped “Remel” swab, see photo). Clinical details must be provided.
Testing will take place in duplicate during the validation process (the second swab will be sent to the National Virus Reference Laboratory Dublin for confirmation). During this period please send 2 clearly labelled swabs where influenza is suspected- one to be a nasal swab and one to be a combined nasal and throat swab.
This test will be available during the core laboratory service 8am to 8pm Monday to Friday and weekends 9am to 12pm.
Please inform the laboratory if testing for other respiratory viruses is clinically indicated."
Dr Deirdre O’Brien, Consultant Microbiologist, MUH
Management
If very unwell (right):
- ADMIT and antivirals ARE recommended
If not particularly unwell
- Symptomatic treatment: Advise fluids and antipyretics (NOTE: aspirin is contraindicated in children)
- Antiviral treatment is recommended in children if <2 years, or if in a defined risk group (above)
- Treatment should be started as early as possible (preferably within 48 hours of onset) but may be started at any time if clinically indicated
Chemoprophylaxis
- Chemoprophylaxis for close contacts is not generally recommended
Unwell child
- Signs of respiratory distress
- Grunting
- Intercostal recession, with chest signs
- ↑ respiratory rate (>50 if <1 year, >40 in 1-5 years)
- Cyanosis
- Severe dehydration
- Altered level of consciousness
- Complicated or prolonged seizure
- Signs of sepsis
- Extreme pallor
- Hypotension
- Floppy infant
Infection control precautions
Hand Hygiene
Alcohol rub/gel and or soap and water if hands are physically dirty. Place a surgical mask on the patient if tolerated.
HCWs PPE
Routine care:
- ≥ 5 years: Surgical mask
- < 5 years: Surgical mask, gloves and apron/gown
Aerosol generating procedure (AGP):
- FFP2 or FFP3 mask, gown, gloves and eye protection
Placement
- Assessment in single room if available
- If no single room, maintain at least 1metre separation from other patients where feasible
- Avoid nebulisation in communal areas
NB: Prioritise use of a single room for assessment of patients with ILI. See here for flu activity level.