Click to open tabs
Anatomy



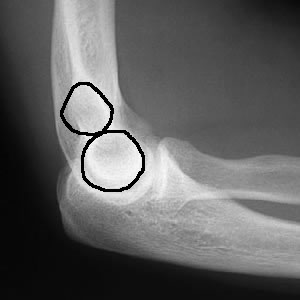
The figure of 8 should be symmetrical = indicating a true lateral view
Fat pads
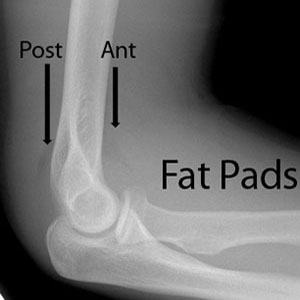
A small anterior fat pad may be normal
An abnormal anterior fat pad "sail" is caused by blood or inflammatory fluid within the joint space
In trauma, a positive fat pad sign = intra-articular fracture
Posterior fat pad is always abnormal
In trauma, any visible posterior fat pad = intra-articular fracture
Anterior humeral and radiocapitellar lines
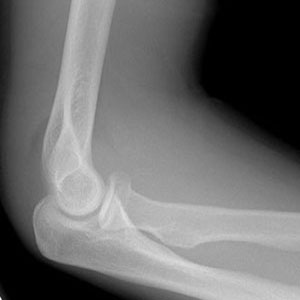
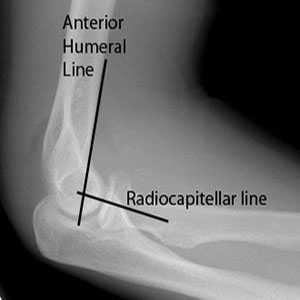
The Anterior Humeral Line should intersect the middle third of the capitellum on the lateral view. If not true, suspect a supracondylar fracture.
The Radiocapitellar line (through centre of the proximal shaft of the radial neck) should bisect the capitellum in ALL views (even oblique). If not, then there is radial head dislocation, requiring immediate reduction.
Bone cortices
Check for evidence of a fracture, particularly along the cortex of the distal humerus (especially children) and the radial head / neck.