Trigeminal neuralgia
Background
- Sudden and severe pain of trigeminal neuralgia as a lightning pain in the face
- "tic doloreux" describes the pain that may be triggered by touch or cold
- Incidence 5 /100,000, Women > Men, Onset often after 60 years of age
- Bouts lasting weeks, remissions lasting months or years
- Probably caused by compression of the trigeminal nerve root, close to the pons, by an aberrant arterial or venous loop
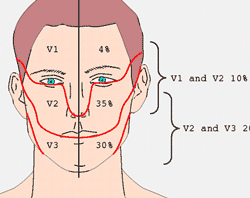
- 1% have involvement of all three nerve branches
- About 2% of patients with trigeminal neuralgia have multiple sclerosis
Differential Diagnosis
- Dental infection or cracked tooth (well localised to tooth, local swelling and erythema)
- TMJ pain (often bilateral, may radiate around ear neck, limited jaw opening)
- Idiopathic facial pain (often bilateral, outside trigeminal territory, pain continuous & milder.)
- Migraine (aura, severe unilateral, assoc GI upset, photophobia)
- Temporal arteritis (constant pain, jaw claudication, fever, wt loss, tender non pulsatile temporal arts)
Treatment
- Standard first line treatment is Carbamazepine (NNT 2.6 v
placebo) [Evidence
Based Neurology]
- 2nd line: if carbamazepine not effective, antidepressants are useful in neuropathic pain (NNT <5) [Bandolier 2008]
- Other drugs including Lamotrigine, Phenytoin, Gabpentin, Oxcarbazine, Topiramate, Baclofen, and Clonazepam
- For management of chronic pain please see Neuropathic Pain page in the analgesia section
Other interventions:
- Microvascular decompression (surgical)
- Methods producing a partial trigeminal nerve lesion
- Neurectomy, radiofrequency thermal ablation, balloon compression, glycerol injections, and radiosurgery
Content by Dr Íomhar O' Sullivan. Last review Dr ÍOS 15/04/24.
