Background
- Intussusception is the invagination of a proximal segment of bowel into the distal bowel lumen
- The commonest occurrence is a segment of ileum moving into the colon through the ileo-caecal valve
- Any age but commonly in the 2 month to 2 years (peak 5 to 9 months)
- M:F = 2:1
History
- Intermittent severe, colicky (child drawing up the legs)
- Episodes 2-3 times/hour and may increase over the next 12-24 hours
- During these episodes of crying the child may look pale (note: many other causes of infant crying are associated with facial redness rather than pallor)
- Pallor & lethargy may be the predominant or persistent rather than episodic, and in some the crying episodes may not be very vigorous
- Vomiting usually prominent (bilious vomiting late)
- Bowel motions
- Blood and/or mucus
- Classic red currant jelly stool is a late sign
- Diarrhoea is common and can lead to a misdiagnosis of gastroenteritis
- There may be a preceding respiratory or diarrhoeal illness
Examination
- Pallor, lethargy - may be intermittent, and may look well in between episodes
- Abdominal mass - sausage shaped mass RUQ or crossing midline in epigastrium or behind the umbilicus, palpable in ⅔ of children
- Distended abdomen later
- Stool:
- Bloody stool/occult blood positive
- PR unnecessary if good evidence of intussusception; abdominal mass or PR bleeding, but otherwise should be done for signs of PR blood or mass
- Signs of an acute bowel obstruction
- Hypovolaemic shock is a late sign
Investigations
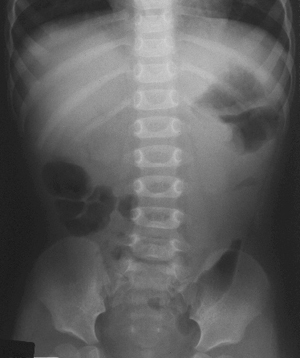
Plain abdominal X-ray
- Performed to exclude perforation or bowel obstruction
- A normal AXR does not exclude intussusception
Signs of intussusception on a plain Xray include:
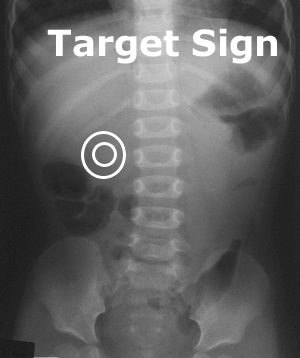
- Target sign - 2 concentric circular radiolucent lines usually in the RUQ
- Crescent sign - lucency usually in the LUQ with a soft tissue mass
Gas insufflation enema (or contrast enema)
- Diagnostic investigation of choice if high level of suspicion
- This intervention is both diagnostic and therapeutic
Ultrasound
- Useful if suggestive Hx but no mass palpable or signs on plain AXR
Labs
- Blood glucose
- Blood group and hold prior to theatre
- FBE and U&E may be useful if child looks unwell
Management
- If shocked see resuscitation guidelines
- Involve surgeons early
- Secure IV access:
- Most require resuscitation with NS 20mls/kg IV
- Keep nil orally
- Pass NG tube if bowel obstruction on AXR
- In general:
- Ilioileal intussusception = treat conservative
- Iliocaecal = intervention