Background
There are 5 common meningococcal serogroups – A,B,C,W,Y.
In March 2025, the
Clinical
History
- Headache/Photophobia
- Neck & back stiffness
- Vomiting/off feeds
- Lethargy/altered conc
- Irritability (infant)
- Fever
- Rash (meningococcal)
Classic clinical features of meningococcal disease can appear relatively late in the illness, early clinical features include:
- Leg pains
- Cold hands & feet
- Abnormal skin colour
Examination
- Ensure Airway is clear, breathing pattern ok
- Circulation pulse rate & vol, BP, cap. refill
- Pyrexia
- Skin Changes / Rash (meningococcal)
- Meningism
- Bulging Fontanelle
- ↓ Level Conc
- Signs of ↑ICP:
- Fluctuating level of conc
- ↑BP & relative bradycardia
- Pupils unequal or focal neurology
- Seizures or Posturing
- Papilloedema (late)
Suspect Sepsis if
- Tachycardia, low volume pulse
- Capillary refill (>3 sec)
- Skin to core temp difference
- Evolving rash
- Oliguria (<1ml/kg/hr)
- Hypotension (late sign)
Suspect Cerebral Oedema
- Na+<135mmol/L & signs of ↑ICP
- or
- Na+<130mmol/l without clinical signs
Beware
Bad Prognostic Signs
- Differential skin/core temp > 3O°C (children)
- SBP < 85 mm Hg (age > 4yrs)
- SBP < 75 mm Hg (age < 4yrs)
- WCC <10.0 x109/L
- Meetab. ↓pH (BE > -5.0 mmol/l or Lactate climbing)
- Coagulopathy
- Rapidly evolving characteristic rash
- Glasgow meningococcal prognostic score (GMPS) > 8
Algorithm
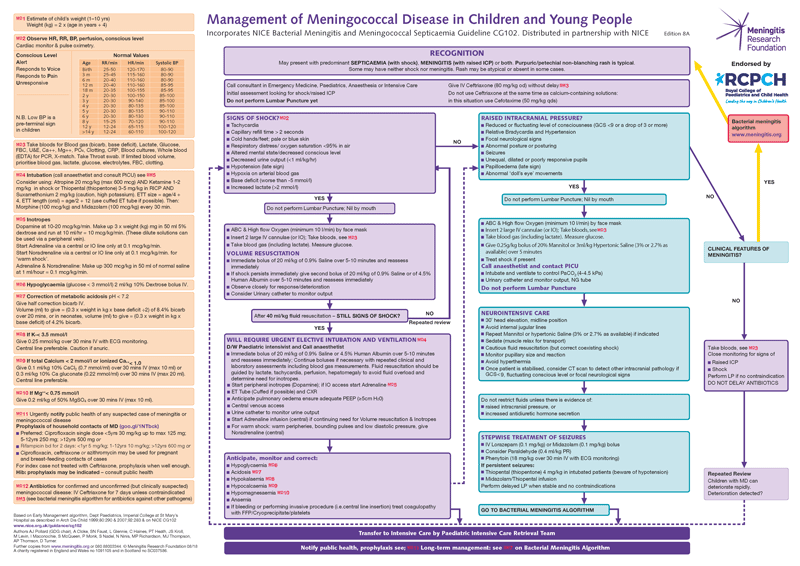
Pre-hospital Antibiotics
The doses of benzylpenicillin (ideally IV but can give IM, although may not be as effective) for GP use in suspected meningococcal infection are tabled:
| Adults & children > 10 yrs | 1200 mgs |
| Children 1 - 9 yrs | 600 mgs |
| Children < 1 yr | 300 mgs |
Links
- Early management of meningococcal disease
- Invasive meningococcal disease in Ireland https://www.hpsc.ie/a-z/vaccinepreventable/invasivemeningococcaldisease/
- Meningitis.org ID and Mx by ambulance personnel (Ireland)
- Meningitis.org Mx bacterial meningitis in children
- Meningitis.org Mx meningococcal disease in children
- Meningitis.org Mx bacterial meningitis in children <3 months
- meningitis.org/