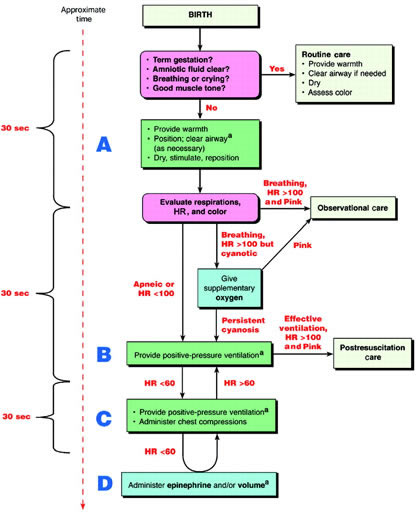
 2005 American Heart Association (AHA) Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) and Emergency Cardiovascular Care (ECC) of Pediatric and Neonatal Patients: Neonatal Resuscitation Guidelines
2005 American Heart Association (AHA) Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) and Emergency Cardiovascular Care (ECC) of Pediatric and Neonatal Patients: Neonatal Resuscitation Guidelines
DDx in infant suddenly gone off (day 10) with cyanosis
- PDA closing
- Group B Strep sepsis
- Critical aortic stenosis
- Coarctation
A few clinical notes
- SubXiphisternal impulse = dilated RV (at any age!)
- Hyperoxic test - <10% rise in O2 saturations with 100% O2 or PaO2<150mmHg = Obstruction to pulmonary flow
- PCO2 LOW in cardiac cause tachypnoea
- Pulmonary atresia or transposition, anomalous aorta, coarcatation, hypoplastic left heart, critical aortic stenosis all very well until duct closes at day 10 – sudden – present sudden onset LVF. - Need prostaglandin infusion
- If using PG must intubate as apnoea a side effect during transfer:
- Alprostadil is kept in CUH Resusc. room fridge and is available from the neonatal unit in CUMH
- Alprostadil / Prostin works very quickly
- Usually response in 10-30 min become pink
- PG side effects - apnoea, pyrexia, vasodilation, seizure like activity
- Trial prostaglandin in any doubt / cyanosed / underperfused
Back to Paediatric Resuscitation Algorithm
Links
Recommendations for Irish services dealing with care of the critically ill children is available at www.aagbi.org/pdf/care_of_the_critically_ill_child.pdf (Local copy)