OCTAPLEX ®
Is the PCC of choice used in the Republic of Ireland.
- Octaplex is a pooled plasma coagulation factor concentrate. Each vial contains coagulation factors II (220 – 760IU), VII (180 – 480IU), IX (500IU) and X (360 – 600IU). It also contains protein C, protein S, albumin, heparin and sodium citrate
- Octaplex is licensed for use in the Republic of Ireland for the treatment of bleeding and peri-operative prophylaxis of bleeding in patients receiving Warfarin. It is also licensed for treatment of bleeding and peri-operative prophylaxis in congenital deficiency of any of the vitamin K dependant coagulation factors (FII, FVII, FIX & FX) when purified specific coagulation products are not available
- A vial of Octaplex costs €390. It is a fridge only product
- PCC (Octaplex) provides a more rapid and effective reversal of Warfarin at a lower volume than human plasma
- Side effects relating to the administration of PCC should be carefully outlined to the patient prior to administration – potential adverse effects of PCC are as follows:
- Hypersensitivity or allergic reactions
- Antibodies the prothrombin complex constituents
- Risk of thrombosis
- Rarely heparin-associated fall in platelet count
- Treatment should always be directed at the underlying cause
Viral Inactivation
When medicinal products prepared from human blood or plasma are administered, the possibility of transmitting infective agents cannot be totally excluded. The viral inactivation processes used, solvent detergent treatment and nano-filtration, are considered effective for enveloped viruses such as, Human Immunodeficiency Disorder (HIV), Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) and Hepatitis C Virus (HCV). The measures taken may be of limited value against non-enveloped viruses such as Hepatitis A Virus (HAV) and parvovirus B19.
There is a residual risk of infection from unknown infectious agents and variant Creutzfeldt-Jacob Disease (vCJD).
There are approximately 3,400 donors contributing to each vial of Octaplex. United States donors are used in an attempt to decrease the risk of vCJD.
Appropriate vaccination (hepatitis A and/or hepatitis B) for patients in regular receipt of products derived from human blood or plasma including Octaplex is recommended.
Admin. of prothrombin complex concentrates (PCC)
- To ensure the safe ordering, prescribing and administration of PCC to patients for the emergency reversal of Warfarin in life threatening major haemorrhage and/or emergency surgery (when there is no possibility of delaying surgery for > six hours)
- PCC (Octaplex) should be administered to patients only in accordance with the procedures outlined below
- Advice from a Consultant Haematologist should preferably be sought prior to administration especially in cases of complex coagulation disorders, such as disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), liver disease or hyperfibrinolysis as appropriate drugs such as heparin, antithrombin III, solvent detergent plasma and antifibrinolytics may be considered
- Clinical judgement should be exercised on a case-by-case basis to decide if the potential benefit of treatment with PCC out-weighs that of the potential thromboembolic complications in the following patients:
- Hx of coronary artery disease
- Liver liver disease
- Peri or post-operative
- Those at risk of thromboembolic phenomena
- Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
- It is recommended that vitamin K be administered intravenously in addition to PCC
- PCC should NOT be used for reversal of Warfarin in non-emergency situations.
- Administration of vitamin K and/or reduction or discontinuation of Warfarin is usually sufficient (Please see over-anticoagulation)
PCC (Octaplex) should not be used in patients with:
- Known hypersensitivity to the active substance or any of the excipients
- Known hypersensitivity to heparin or history of heparin induced thrombocytopenia
Prescribing and dose of PCC
- Dosage and duration of therapy depend on the severity of the coagulation disorder, the location and extent of bleeding and the clinical condition of the patient
- Initial bolus doses of 25iu to 50iu of factor IX (FIX) per kg body weight are recommended in cases of severe haemorrhage
- As a guideline the recommended dose of Octaplex is based on the factor IX (FIX) content of Octaplex and the patient’s International Normalised Ratio (INR)
| Patient’s INR | Dose of Octaplex based on FIX content |
|---|---|
| INR 2.0 – 3.9 | 25 IU/kg |
| INR 4.0 – 6.0 | 35 IU/kg |
| INR – 6 | 50 IU/kg |
A single dose of Octaplex® should NOT exceed 3000 IU (i.e. 120 mL Octaplex®)
If the calculated dose exceeds 3000 IU, administer 3000 IU then repeat the INR and seek advice from haelatology.
Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs)
Octaplex® is not licensed for the reversal of anticoagulation due to the anti-Xa inhibitors (e.g. Apixaban, Rivaroxaban, and Edoxaban) and is not recommended for this purpose. However, it is occasionally used in life threatening haemorrhage in the absence of a specific reversal agent.
The local policy on the management of adult patients on direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) in CUH Group (PPG-CUH-CUH 267) recommends that in cases of life threatening bleeding, 2000 IU of PCCs should be administered to patients on Xa inhibitors (e.g. Apixaban, Rivaroxaban, and Edoxaban). The haematology team should be contacted if the patient continues to bleed.
Patient Consent
- The doctor should explain that PCC (Octaplex) is to be administered
- The benefits and risks associated with the proposed PCC and alternative treatment options (including no treatment) should also be explained (see overview, pg.1)
- If possible verbal consent should be obtained from the patient and documented in the patients medical notes
Ordering & storage
- PCC (Octaplex) should be prescribed on the CUH Blood Component And Blood Product Prescription and Transfusion Record. (Form No. 15)
- The reason for the prescription should be clearly documented
- A Blood Product Requisition Form needs to be completed with : patients’ name, medical record number, date of birth, ward, date and time of request, reason for transfusion, most recent INR & APPT result
- Send requisition to the Blood Transfusion Laboratory
- Phone the laboratory to confirm receipt of requisition
- PCC (Octaplex) is issued with a “cross match compatibility form” from the Blood Transfusion Laboratory containing the batch numbers for inclusion in the patient’s medical record to facilitate traceability
Monitoring response
- An INR must be taken within thirty minutes to one hour after administration of PCC (Octaplex)
- The INR should be monitored every 4-24 hours until the patient’s INR is within their target range
Beware of tachycardia
- If there is a marked increase in the pulse rate during administration the injection speed must be reduced or the administration stopped
- The suggested rate of administration of PCC (Octaplex) is 1ml/minute
Reconstitution
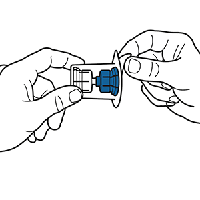
Remove the top of the Mix2Vial package. Do not remove the device from the package.
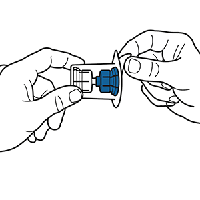
Seat the blue end of the device on the water vial, using the blister pack as a holder. Push down until the spike penetrates the stopper and the device snaps in place.
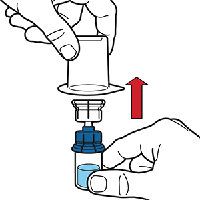
Remove the plastic package and discard it. Take care not to touch the exposed end of the device.
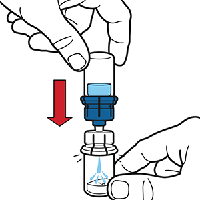
Turn the water vial upside down and insert the clear end into the powdered Octaplex® vial, pushing down until the spike penetrates the stopper and the device snaps in place.
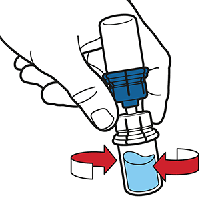
The water will automatically flow into the Octaplex® vial. Gently swirl the vial to make sure the Octaplex® is thoroughly mixed.
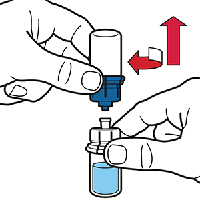
Remove the water vial by turning it anticlockwise. Attach a syringe to the Octaplex® vial.
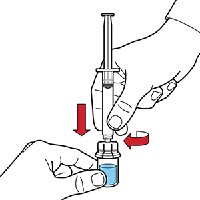
Turn the Octaplex® vial upside down and withdraw the solution into the syringe. Remove the syringe by turning the barrel counter clockwise. Octaplex® is now ready for administration.
References
- Octapharma Ltd., (2004). Octaplex Republic of Ireland Product Characteristics. Coventry: Octapharma Ltd
- Lubetsky A. et al. (2004). Efficacy and Safety of a Prothrombin Complex Concentrate (Octaplex) for the Rapid Reversal of Oral Anticoagulation. Thrombosis Research. 113, p. 371-378
- Preston F.E. et al. (2002). Rapid Reversal of Oral Anticoagulation with Warfarin by a Prothrombin Complex Concentrate (Beriplex): efficacy and safety in 42 patients. British Journal of Haematology.116, p.619-624
- Evans G. et al. (2001). Beriplex P/N Reverses Severe Warfarin-induced Anticoagulation Immediately and Completely in Patients Presenting with Major Bleeding. British Journal of Haematology. 115, p. 998-1001
- Makris M. et al. (2001). The Management of Coumarin-induced Over-Anticoagulation. Annotation. British Journal of Haematology. 114, p. 271-280