Background
- Any fluid or drug that can be given IV can be given IO
- If rapid fluid replacement is required infuse under pressure using a 50 ml syringe
- Dilute strong alkalis and hypertonic solutions
- After giving drugs IO, flush them through
- Blood drawn from an IO needle can be used for x-match and biochem.
Equipment
- Something to clean the skin
- Intraosseous needle
- 20 ml syringe filled with normal saline
- Short extension set and 3 way tap
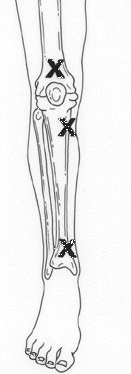
Procedure - manual needle
- Identify the appropriate site
- Avoid fractured bones, or limbs with proximal fractures
- If possible avoid areas of burns or of skin infection
- Proximal tibia: Anteromedial surface, 2-3 cm below the tibial tuberosity
- Distal tibia: Proximal to the medial malleolus
- Distal femur: Midline, 2-3 cm above the external condyle
- Prepare the skin
- For a non-screw-in needle
- Insert the needle through the skin, and then with a screwing motion perpendicularly / slightly away from the growth plate into the bone
- There is a give as the marrow cavity is entered
- For a screw-in needle the give may be less pronounced
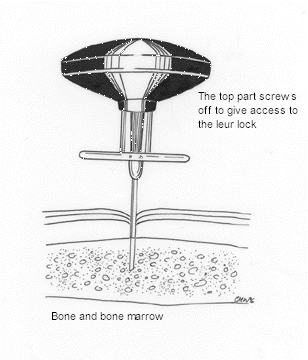
Procedure - EZ-IO
Once needle inserted (manula or ez-io), please:
- Remove the trocar and confirm position by aspirating bone marrow
- Marrow cannot always be aspirated but it should flush easily
- Secure the needle and start the infusion
Contraindications
- Proximal ipsilateral fracture
- Ipsilateral vascular injury
- Osteogenesis imperfecta
- Osteoporosis
Complications
- Failure to enter the bone marrow, with extravasation or subperiosteal infusion
- Through and through penetration of the bone
- Osteomyelitis (rare in short term use )
- Growth plate injury
- Local infection, skin necrosis, pain
- Compartment syndrome, fat and bone microemboli have all been reported but are rare
Links
- IAEM Adult-IO-Guideline-V1, Dr Micheál Sheehan 2023
- EZ-IO manufacturer's pocket guideline
- List of drugs that can be given IO
Acknowledgements
The artwork is by Caroline Wilkinson, and is published with the permission of the BMJ Publishing Group.