The Level 1 system can warm fluid to a temperature of close to 37° Celsius and infuse fluids at rapid rates. These rates depend on the size of the cannula used.
| Administration of Crystalloids under pressure (300mmHg) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cannula Size | Flow rate (ml/min) | Elapsed Time (min/L) |
| 18g | 240 | 4.2 |
| 16g | 440 | 2.3 |
| 14g | 500 | 1.7 |
| Administration of Packed Red Cells under pressure (300mmHg) | ||
| Cannula Size | Flow rate (ml/min) | Elapsed Time (min/L) |
| 18g | 150 | 2.3 |
| 16g | 220 | 1.5 |
| 14g | 300 | 1.1 |
Procedure
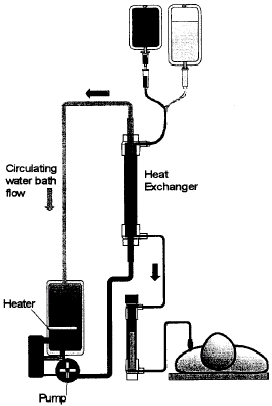
- Place the bottom end of the heat exchanger (blue metal tube) into the slot marked ‘1’
- Place the top part of the heat exchanger into the slot marked ‘2’ until it clicks
- Insert the filter into the slot marked ‘3’
- Ensure all connections are secure
- Close all IV clamps
- Spike the IV fluid bags and hang them on the hooks provided
- Open the clamp above the drip chamber and half fill the chamber
- Open the rest of the clamps and prime the remainder of the giving set
- Once the giving set is adequately primed, close the doors of the infuser
- Plug in and turn on the infuser. The green button is the on button
- Connect the IV tubing to the patient
- To infuse the fluid under pressure, push the switch from (-) to (+)
- All fluid administered using this infuser will be heated to close to 37°
- Once the fluid is infused, turn the switch from (+) to (-). Close the clamp above the drip chamber. Replace the fluid with a new bag if required
- Repeat procedure as required
- To turn off the infuser, press the orange button (next to the green button!)
Equipment required
- Level 1 Rapid Infuser (instruction manual)
- D-50 fluid giving set
- Fluid/Blood products
Infusion of blood products
For blood products, or 500ml bags of IV fluids, use the hook on the inside of the door. Otherwise, repeat as above.
Use of non-collapsible containers (e.g. Gelofusion)
It is essential to remove any air from these containers prior to administration under pressure to prevent possible air embolism by:
- Venting of the container using a ‘Braun aeration needle’
- Venting of the container using a giving set