Background
- Re-expanding a collapsed lung may result in re-expansion pulmonary oedema(REPO)
- May occur in 1% of cases after draining air, blood or fluid
- More common if large volume (air or fluid) drained rapidly or collection present for some time before drainage
- Re-perfusion of locally hypoxic lung leads to inflammatory response and ↑ local capillary permeability
Clinical
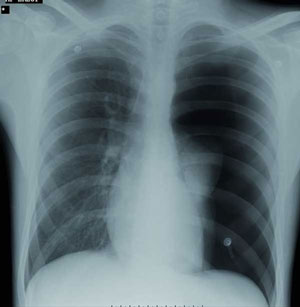
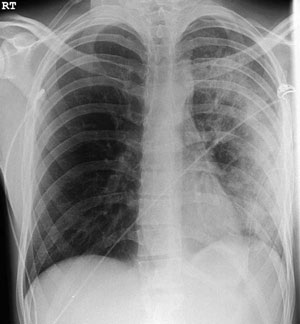
Within 2 hours of thoracocentesis:
- Asymptomatic radiological changes or
- Cough / SOB or
- Frank pulmonary oedema with hypoxia
- Frothy pink (rather than purulent) sputum
Differential Dx
- Infection of the re-expanded lung
Investigations
- CXR confirms unilateral airspace opacification of the re-expanded lung
Management
- Controlled drainage of large pleural effusions by clamping the drain if more than 1.5 L of fluid is drained in the first hour after insertion, or if the patient develops a cough
- Do NOT clamp if draining a pneumothorax
- Treat with oxygen, analgesia, diuretics, CPAP / NIV
- Role of diuretics is controversial