Background
- A presumed compression fracture of the articular cartilage
- A fracture fragment may be attached or detached (loose body in joint) from cartilage
- Injury may be cause a single compression fragment or recurrent micro fractures
- Initial local inflammation with micro fracture
- Subcortical thinning (x-ray epiphyseal sclerosis) and later
- Remodeling with weaker bone (subchondral cysts), compression fracture with loss of cartilage volume
Location
Commonest locations include:
- Knee - med femoral condyle (alt aspect), wt bearing areas both condyles and intercondylar groove
- Rarely patella or tibial plateau
- Elbow - capitellum (? xs valgus stress)
- Ankle - talar dome
- Foot - Navicular (DDx stress #)
- Hip - femoral epiphysis (esp. if PMHx of Perthe's)
- Wrist rare - scaphoid
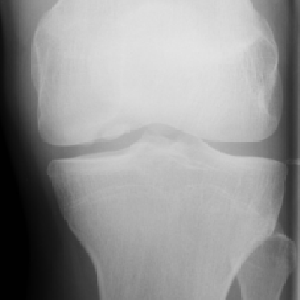
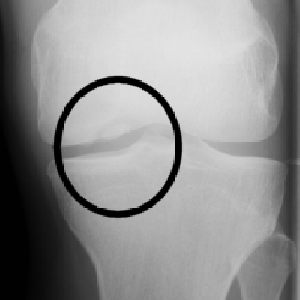
Clinical
- Young adults or teens report pain on wt bearing
- Atraumatic joint pain, (ofetn with effusion) ± locking
- Pain on limit of ROM
- Traumatic effusion and occasional instability
- OA can develop
- Loose body symptoms generally late
Beware
- Frequently missed
- May require CT to confirm
- If in doubt, non-weight-bearing (NWB) & ortho OPD referral