Neurological hints
Dermatomes C6 = thumb & index finger, C7 = middle finger; C8 = ring & little fingers
Meduan Nerve
- Superficial branch of median N. - over thenar eminence.
- Discriminates between a high or low median nerve lesion

- Anterior Interosseous nerve - loss of precise pinch
- (unable to make 'OK' sign, instead make a square)
- due to loss of FPL & FDP to index finger
Ulnar Nerve
- Splay fingers - ADM & 1st dorsal interosseous (DAB), PAD
- Wartenburg's sign - little finger lies abducted (unopposed action of EDM)
- Froment's test – Thumb flexed
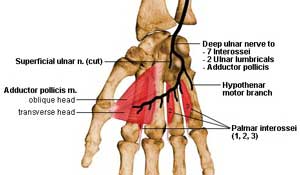
- Ulnar Paradox = less clawing of the fingers than a low lesion
- FDP is involved in high lesions thus flexing MCPJ & relaxing IPJs

Radial Nerve
- Posterior Interosseous nerve - Wrist dorsiflexion results in radial deviation (since ECU supplied by PIN, but brachioradialis & ECRL are supplied by the Radial nerve)
- Superficial Branch of Radial Nerve:
- Wartenburg's Neuritis (compression at the insertion of Brachioradialis)
- Dellon's sign = active forceful pronation of the forearm & ulnar deviation of the wrist with the elbow extended by the side
- Tinel's test at the insertion of Brachioradialis
Tendons
Middle Slip (traumatic Boutonnière deformity)
- Elson's Test. Put finger over edge of table, with PIPJ flexed to 90°& ask Pt to extend against resistance
- Weakness of resisted extension of PIPJ & hyperextension of DIPJ occurs if the central slip is ruptured
- Passive test. Flex wrist & MCPJs. Poor passive resistance to pushing over middle phalanx indicates weak extensor mechanism
| Compartment Contents | Pathologic Conditions |
|---|---|
| APL & EPB | DeQuervain's Disease |
| ECRL & ECRB | Tennis elbow |
| EPL | Rupture at Lister's tubercle |
| EDC & EIP | Extensor Tenosynovitis |
| EDM | Rupture (rheumatoid) |
| ECU | Snapping at ulnar styloid |
Content by Dr Íomhar O' Sullivan. Last review Dr ÍOS 25/04/24.