Viral sinusitis is very common. Bacterial sinusitis should be suspected if symptoms persist for more than 7 days.
- Symptoms - include nasal congestion, purulent nasal discharge, maxillary tooth discomfort, hyposmia or anosmia, cough, facial pain or pressure that is made worse by bending forward, headache, fever, and malaise
- Examination - nasal turbinate oedema, nasal crusts, purulence of the nasal cavity and posterior pharynx, and failure of transillumination of the maxillary sinuses
- Most viral infections improve in 7 to 10 days - persistence of symptoms suggests bacterial sinusitis
- Symptoms of viral sinusitis, including fever, mimic those of bacterial sinusitis, although discolouration of nasal discharge may help differentiate
- Strep. pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae are the major bacterial pathogens in adults (Branhamella (Moraxella) catarrhalis in children)
- Potential complications of include local extension (e.g. orbital cellulitis) and the spread of bacteria to the CNS / cavernous sinus
- Clinical symptoms show poor sensitivity and specificity [Bandolier] (table below)
| Comparison (with sinus puncture) | No. of studies | No. of patients | Weighted prevalence (%, range) | Pos LR | Neg LR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radiography | 7 | 996 | 57 (26-80) | 3.4 | 0.26 |
| Ultrasound | 7 | 940 | 56 (27-80) | 2.8 | 0.3 |
| Clinical examination | 2 | 245 | 46 (44-48) | 3.3 | 0.4 |
- Other reviews have shown that [positive predictive value,negative predictive value]
- "Biphasic illness" is the most useful clinical clue (viral UTRI resolving then recurrence of unilateral symptoms)
- Purulent discharge [62%,78%], Pain on bending fwd [78%,73%], maxillary toothache [59%,56%], pain with chewing [54%,53%] are poor predictors
- Please note that allergic rhinitis is a rare initiating factor
Imaging
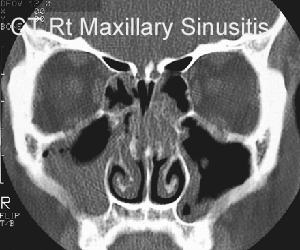
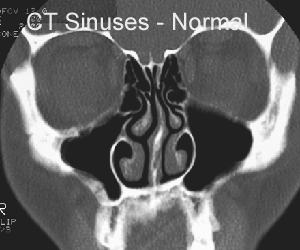
- Plain x-rays or CT have poor sensitivity(76%) and specificity (79%) and are NOT indicated
- May demonstrate - sinus opacity, air–fluid level or marked mucosal thickening
- But cannot differentiate viral from bacterial
Differential diagnosis
- Includes URTI, nasal foreign body
- Dental pain (particularly in cases of unilateral facial pain)
- Neuralgic (atypical) facial pain
- Temporomandibular joint pain
- Migraine, cluster or tension headaches
- Trigeminal neuralgia
- Temporal arteritis
- Neoplastic conditions
Management
- Advise adjunctive treatment in all
- Antibiotics can help relieve uncomplicated sinus infections, but they do not make a major difference on clinical cures [Cochrane review 2005]
- If on balance you decide to use antibiotics, current CUH antibiotic guidelines suggest tetracycline for 10 days
Adjunctive treatment
- Diet (increase fluid intake), steam and local heat are advisable
- No clinical trials have demonstrated any increased efficacy of topical steroids, topical decongestants, oral decongestants, antihistamines or mucolytic agents
- Avoid topical decongestants for > 5/7 as will result in rebound symptoms