Remember analgesia
- Please note mechanism of injury and hand position at "impact"
- Please note hand dominance and occupation
Undisplaced # of distal radius incl. greenstick #
- Splint or backslab & sling. In CUH VFAC (green) follow up
Fractures of the ulnar styloid
- No active treatment required
- Splint for comfort, sling
- In CUH VFAC (green) referral
Scaphoid injuries
- Commonest (70%) carpal # (then triquetral & trapezium)
- FOOSH with hyper-extension of the wrist
- Initial x-ray (full scaphoid series):
- Specificity is 100%, Sensitivity is 80%
- 1 of 4 people with a negative initial x-ray have a #
- In CUH: refer to ANP clinic in the ED (@10/7). If still symptomatic but x-rays negative on review at 10 days: refer to VFAC
| Sign | Pos LR [95%CI] | Neg LR [95% CI] |
|---|---|---|
| Clamp sign * | 8.6 [0.51-147] | 0.54 [0.14-1.18] |
| Resisted supination pain ** | 6.1 [0.04-10.86] | 0.09 [0.00-11.9] |
| Thumb compression pain | 2.0 [1.1-3.5] | 0.24 [0.06-0.99] |
| Scaphoid tubercle | 1.7 [1.3-2.1] | 0.23 [0.09-0.56] |
| Snuff box tenderness | 1.5 [1.1-2.1] | 0.15 [0.05-0.43] |
| Ulnar deviation pain | 1.4 [0.8-2.4] | 0.53 [0.13->1] |
| * Clamp sign : ask patient "exactly where does it hurt?". The patient will form a clamp with the opposite thumb and index finger on both sides of the thumb. | ||
| ** Pain with resisted supination: Hold the injured hand with forearm in neutral position. Patient attempts supination = pain when examiner resists | ||
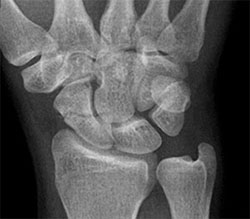
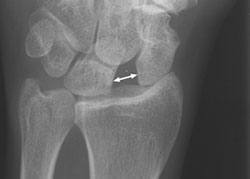
(Terry Thomas sign)
In CUH
- Radiologically confirmed scaphoid #s should be treated by scaphoid POP, sling & # clinic
- Refer to ortho for ORIF if > 1mm displacement of fragments, angulation ≥15%, # comminution
- Check x-rays for signs of ruptured scapholunate ligament. (Terry Thomas sign)
- If seen, confirm again no evidence of carpal dislocation and treat as a scaphoid fracture
Colles' fracture
- Refer to senior ED staff for anaesthetic technique if manipulation required
- Manipulate as instructed under Bier's block or analgesia and sedation. Remember traction (often forgotten), flexion, pronation and ulnar deviation makes your job (and result) much easier
- Apply POP backslab and sling
- Obtain check X-rays. Refer to VFAC
Indications for manipulation rather then backslab (& # clinic referral) include:
- > 10° dorsal angulation (tilt)
- Radial shortening > 3 mm (important)
- Radial shift more than 2 mm
- Dorsal displacement more than 2 mm
"Rules" may not apply in some (elderly e.g.). Please discuss with your EM senior if in doubt.
Smith's fracture
- Usually require internal fixation (refer to on-call orthopaedic team)
- If not, manipulate under LA/sedation by disimpaction, supination, extension and ulnar deviation and apply ventral POP slab. Obtain check X-rays. Extend slab anterolaterally over the upper arm to form an above elbow slab and keep forearm supinated. Provide sling and refer to the Fracture Clinic
Barton's fracture
- Displaced intra-articular fracture of the distal radius
- Often requires MUA
- Beware neurovascular compromise - always check median nerve function and advise immediate return if symptoms
- If reduction not ideal - refer to on-call Orthopaedic Team
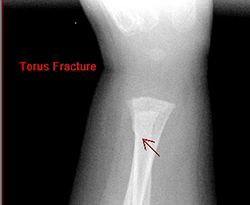
Torus (buckle) fractures distal radius
- Torus # of the distal radius in children should be splinted
- In CUH please refer to "VFAC Green"
- Please ask parents to remove the splint in a few days & see if their child is symptom free
- If concerns, please return to the ED/LIU. advice sheet
Other carpal fractures
- Immobilise in backslab, sling and refer to the VFAC
- Commonest is flake triquetral fracture seen on dorsum carpus lateral view:
- Triquetral complication : deep branch ulnar nerve : beware early ulnar motor signs
Wrist or carpal dislocations
- Check neurovascular status (particularly median nerve)
- Refer to the on-call Orthopaedic team
References & Links
- Phillips TG, Reibach AM, Slomiany WP. Diagnosis and management of scaphoid fractures .Am Fam Physician 2004; 70(5):879
- Freeland P. Scaphoid tubercle tenderness: A better indicator of scaphoid fractures? Arch Emerg Med 1989; 6(1):46
- Chen SC. The scaphoid compression test. J Hand Surg Br 1989; 14(3):323
- Powell JM, Lloyd GJ, Rintoul RF. New clinical test for fracture of the scaphoid. Can J Surg 1988; 31 (4):237
- Ring D, Jupiter JB, Herndon JH. Acute fractures of the scaphoid. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2000; 8(4):225
- Carpenter CR et al. Adult scaphoid Fracture. Acad Emerg Med 2014;21(2):102-21 (AliEM link)