All older patients presenting to the ED should be routinely asked if they have fallen in the past year
Background
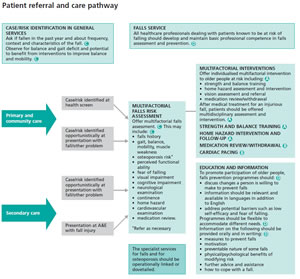
- Those considered at risk of falling should be observed for balance and gait deficits and considered for their ability to benefit from interventions to improve strength and balance. Tests of balance include:
- Timed Up 'n Go (TUG)
Beware those who:
- Have fallen more that once
- More that 5 medications
- Needed assistance to get up off floor
Consider referring recurrent fallers or high risk patients to the CREST or geriatric out patients. Multifactorial assessment may include:
- identification of falls history
- assessment of gait, balance and mobility, and muscle weakness
- assessment of osteoporosis risk
- assessment of the older person’s perceived functional ability and fear relating to falling
- assessment of visual impairment
- assessment of cognitive impairment and neurological examination
- assessment of urinary incontinence
- assessment of home hazards
- cardiovascular examination and medication review
Approach
| Intrinsic Fall Risk factors | Extrinsic Fall Risk factors |
|---|---|
| Previous fall/fear of falling | Footwear or foot problems |
| Advanced age | Home hazzards |
| Chronic conditions | Improiperuse of assistive devices |
| Cognitive impairmenty | Multifocal eyeglasses |
| CVS abnormalities | New glasses prescription |
| Gait and balance problems | Substance use |
| Orthostatic hypotension (measuring) |