Elbow x-rays
When reviewing elbow x-ray please check:
- Fat Pads (see white arrows in left image)
- Anterior humeral line (throu' ant / mid 1/3 capitellum)
- Radiocapitellar line (Radial shaft alignment with capitellum in ALL views)
- C R I T O L capitellum, radial head, internal epicondyle, trochlea, olecranon, lateral epicondyle
Please see upper limb x-rays for more
Dislocation of the elbow
- Needs urgent reduction.
- Call senior ED staff before admit ortho
- Document neurovascular status
Fractured olecranon
- Admit ortho for ORIF (wires)
"Pulled Elbow"
- Child (1 to 6 years). Hx of traction injury, not using arm (often kept "limp" in extension and pronated - almost "waiters tip")
- No signs clavicle, shoulder or wrist injury
- Poorly localised elbow tenderness. Pain on elbow movements especially rotation
- Pronation with or without elbow flexion is the first line method of reduction for pulled elbows [BestBets]
- Listen or feel for click. Leave child for a few minutes and then observe function
- If no recovery consider X-ray and if normal X-ray, ask to return after one day if not using arm normally
Supracondylar fracture of humerus#
- In all children check (1) Fat pads (2) Ant humeral line (3) Radiocaptetellar line (4) CRITOL (please see x-rays section)
- Check and record neurovascular status
- Popliteal art. damage, or Ant Interosseous (median) Nerve - Ok sign?
- Simple undisplaced fractures may be placed in a sling or full length POP (90°) depending on comfort
- Please discuss each case with your ED aenior
- If necessary admit orthopaedics

Supracondylar #
Gartland classification
I : undisplaced or minimally displaced.
II : displaced but with intact cortex.
II a: posterior angulation with intact posterior cortex; anterior humeral line does not intersect capitellum.
III : completely displaced.
# neck/head of radius
- Check radial pulse
- Assume an intra-articular (or supracondylar) if mal-alignment or effusion seen
- Treat fractured head of radius with analgesia and a broad arm sling
- If gross displacement / comminution refer to on-call Orthopaedic Team
- Therapeutic aspiration is not our routine practice [BestBets]
- Otherwise refer to the next Fracture Clinic
- Repeat radiography is not needed for traumatic elbow effusions with no fracture on initial x-ray [BestBets]
Radial Head / Neck # Mason Johnston Classif.
I - Nondisplaced
II - Minimally displaced with depression, angulation and impaction
III - Comminuted and displaced
IV - Radial head # with dislocation of the elbow
Lateral epicondyle
- Usually FOOSH
- Record neurovascular findings
- Check C R I T O L, lines and fat pads
- Typically Salter Harris iv
- Often subtle x-ray findings, sometimes just positve fat pads
- Consider oblique or X-ray in children
- Refer Ortho. These fractures have poor prognosis (mal/non union). Undislaced fractures may be treated (after ortho consult) in a above-elbow PoP (90° flex) and fracture clinic. Any rotation or displacement (esp if >2mm) need surgery (ORIF) today
- High incidence long term valgus deformity with delayed ulnar N. palsy


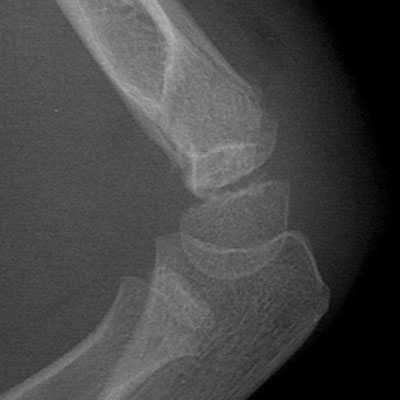
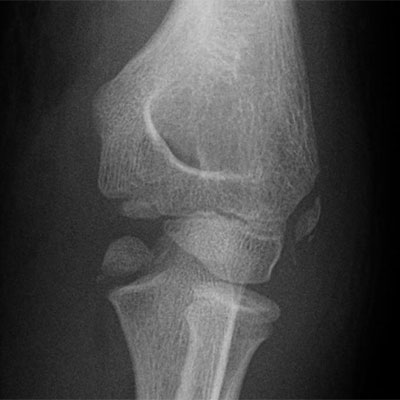
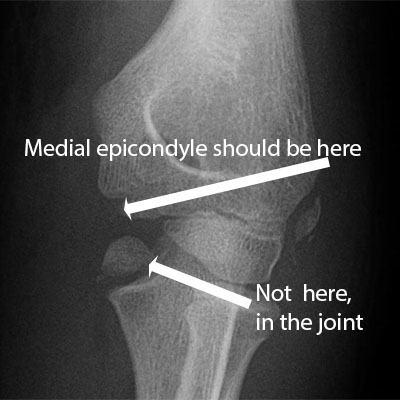
Medial epicondyle
- Usually pull off # with valgus stress on elbow (beware dislocation)
- May not have fat pad sign (extra-articular)
- Beware intra-articular condylar # (all need ORIF) rather than epicondyle #
- Surgery now if >15 mm displacement, med epicondule in joint (easily missed)
- Record neurovascular examination findings
- Always check C R I T O L, Ant Humeral line, Radiocapitellar line and fat pads
- Minimal displaced medial epicondylar # = PoP backslab (90° flexion) and fracture clinic follow up
- Displaced #, elbow dislocation or intra-articular condylar # = ortho referral now for ORIF
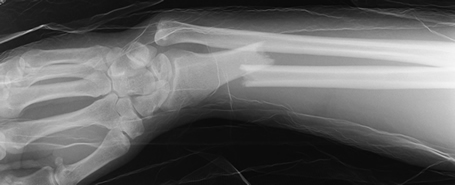
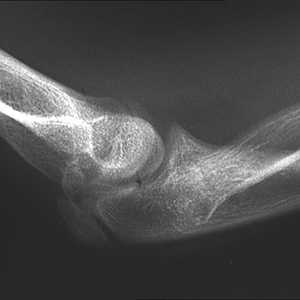
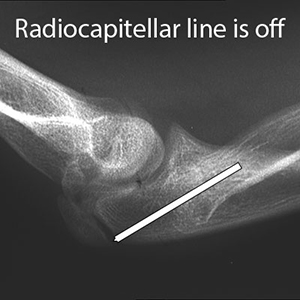
Dislocated head of radius (abnormal radiocapitellar line)
- Radiocapitellar line should be good in all x-rays
- Often with # of ulnar shaft (Monteggia fracture-dislocation)
- X-rays of the whole forearm are required
- Beware neurovascular (particularly radial N motor fxn)
- Admit ortho for ORIF
Forearm
Fractured shaft of radius and ulna
- Refer to on-call Orthopaedic Team
- MUGAR (Monteggia - Ulna #, Galeazzi - Radial #)
Dislocated head of ulna
- Usually associated with a fracture of the radial shaft (Galeazzi fracture-dislocation - image right) and X-rays of the whole forearm are required for diagnosis
- Refer to on-call Orthopaedic Team