Thumb MC #
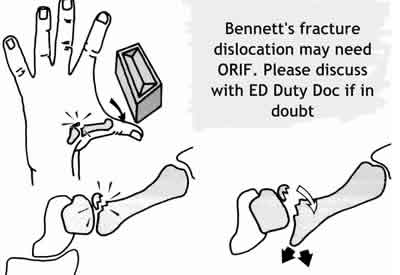
Fractures of the base of the thumb metacarpal not involving the joint need to be differentiated from fracture dislocations or subluxation (Bennett's #)
- Treat Bennett's fracture-dislocation with : Bennett's POP and refer to the on call orthopaedics. Good initial reduction is important. Thereafter, there is no significant evidence between surgical and conservative management approach. [BestBets]
- Fracture base thumb MC not involving joint : Thumb spica or Bennett's POP and fracture clinic (Referral form). Sling
Ruptured Ulnar Collateral Ligament (UCL) thumb MCPJ (Gamekeeper's thumb)
See link above or Here
Index - Ring metacarpal fractures
Usually undisplaced. Treat with bandage and a sling and refer to the Fracture Clinic. If displaced, ask for advice.
Punch Injuries
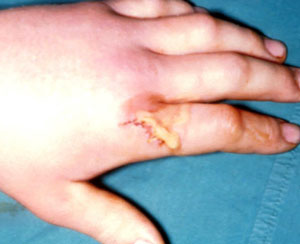
- Beware apparently innocuous injuries
- If the skin in breached, assume the joint space and or extensor tendon have been breeched until proven otherwise
- X-ray all (FB)
- Detail neurovascular and tendon (including middle slip) status
- Treat abrasions with antibiotics and treat as needlestick injury
- All deep wounds need referral to ortho for formal exploration and washout
Little metacarpal fractures
- Usually displaced.
- Treat with neighbour strapping and early mobilisation in preference to Edinburgh slab [BestBets] and sling
- Refer to the Fracture Clinic at CUH Referral form
- Severely displaced fractures may benefit from K wire
- If in doubt ask ED Duty Doc
Proximal metacarpal injuries
Most are stable injuries if sustained with a clenched fist (no rotation at the time of injury) but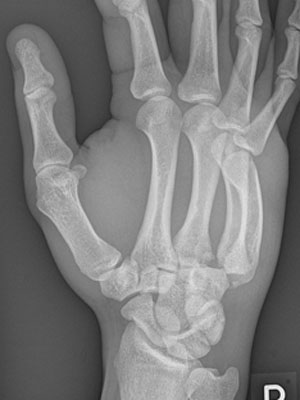
Beware of a proximal (carpometacarpal) dislocation.
- Tender over the proximal metacarpal ( and carpo-metacarpal area)
- Deformity may appear subtle
- Usually no rotation
- As with most other limb view scrutinise the lateral view for deformity or unusual appearance
Dislocation of PIP and DIP joints
- Confirm with X-ray (exclude fracture).
- Reduce under LA. Assess stability (AP side-to-side).
- If stable, apply a Bedford splint, sling and refer to the fracture clinic (Referral form)
- If unstable, refer to the on-call orthopaedic Team
- Always do a post reduction x-ray
Volar plate injuries
- Hyperextension injury
- Ligament may avulse chip off base mid phalanx by the volar plate
- Undisplaced small chips heal without problems
- Larger (> 25% artic surface) or comminuted fragments best internally fixed - check with the ED Duty Doc if in doubt
- Check for and document any co-existing collateral ligament damage
- Neighbour strap and encourage early joint mobilisation
- Refer to fracture clinic Referral form)
Phalangeal fractures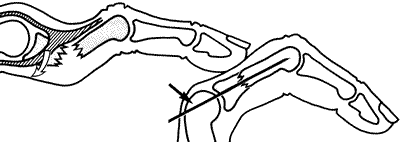
- Transverse fractures of the prox phalanges are unstable (often need fixing)
- Discuss with your ED Duty Doc
- Spiral fractures are also unstable and particularly prone to rotation.
- ANY rotation deformity must be corrected and splinted in a position of anatomical function before discharge from the department.
- All spiral fractures are followed up in the next fracture clinic.
- Refer to your ED Duty doctor and / or on-call ortho SpR if reduction not achieved
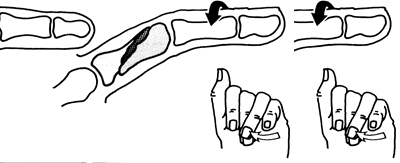
- Displaced finger fractures involving the joint should be referred to the orthopaedic team on call
- Open fractures other than those of the tuft require immediate referral.
- Those of the tuft require wound toilet and anti-staphylococcal antibiotics
Mallet finger
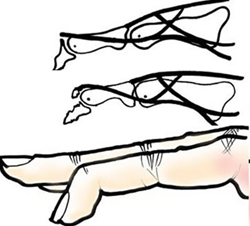
- More Info Here
- X-ray to look for avulsion fracture (better chance of healing)
- With a large fragment check that the DIP joint is not subluxed
- Check that PIPJ is not gong into hyperextension (occurs in small % of those with mallet) - will need to be treated if present
- General management includes : Apply a mallet (stack) splint full-time for 6 weeks, then at night for 2 weeks. GP or plastics clinic follow up. Follow 2 week rule - if extension lag at any time then return to splint full time for another fortnight
- If splint is removed the finger must be kept straight even when washing
- Explain the prognosis - (1/2 left with deformity even if in splint) but that the function of the hand / finger will not be effected. Warn the patient that it may not heal. Patients with exceptional hand requirements may be referred to the fracture clinic or plastic clinic
- It is important that the mallet splint allows for full flexion at the PIP joint and patients are encouraged to mobilize at the PIPJ level
- If the joint is subluxed please refer to the on-call orthopaedic team
Boutonnière finger
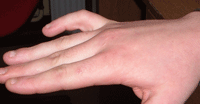
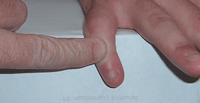
Finger extensor tendon normally has two lateral slips (inserting into distal phalanx) and a middle slip inserting into the base of the intermediate phalanx. If this middle slip ruptures the patient may have point tenderness as the site of the rupture and a "button hole" or Boutonniere deformity ensues. Patients will be unable to extend the PIPJ flexed over the edge of a table (and will have hyperextension of the DIPJ). Apply splint to hold the PIPJ straight and refer to the next CUH fracture clinic.
Ruptured or lacerated extensor or flexor tendons or digital nerve injury
- Refer to on-call plastic surgery team.
- Remember the relative importance of digits (thumb/little finger), patient's occupation and hobbies, dominant hand
Spreading or deep hand infections
- Refer to senior staff or on-call Plastics (particularly tenosynovitis)
- Extensive soft tissue trauma, e.g. severe burns, digital amputations - refer to ED Duty doctor
- Only refer to the orthopaedic team after discussion with your ED senior
Trapped fingers and amputated
finger-tips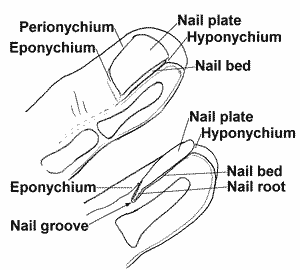
Trapped finger tips with partial avulsion should rarely be sutured:
- Clean gently, reposition and hold in place by Ethistrip or Steristrip, with the ends anchored by 'clear tape'. In most cases this should be done by the doctor, but in any case the position must be checked by the doctor
- Leave the nail in position (Tinct. Benzolin on skin to help adhesion)
- Do not put strips all around the finger
- Put on a non-adherent dressing
- Over this put a bandage
- Check the immunisations are up-to-date
- Only give antibiotics if the wound cannot be thoroughly cleaned [BestBets]
- Leave for at least 3 days
- Warn the patient (parent) that the finger will look awful at the first dressing
- Either bring the finger injury back to the ED clinic in a further 3 to 4 days (remove top dressing only) or refer back to the GP
- Do not discharge the patient until you are satisfied that function is full
Guillotine amputations of finger tips
Terminal amputations of the finger tips in young children do extremely well with conservative treatment only. Even if the bones protrude slightly it should be left alone:
Remember analgesia - soak fingertip in 1% lignocaine with adrenaline for several minutes.
- They should be cleaned thoroughly
- The finger is covered with several layers of Tulle Gras and Jelonet and a mitten bandage is applied
- Leave alone for 2 to 3 days. Then back to GP or dressing clinic
- Warn the mother that it will look awful but should do very well.
- Give advice sheet with photographs
- Do not give any antibiotics but check tetanus immunisation
There should be regrowth of the tip and nail and complete restoration of function with an excellent cosmetic result eventually (look at series of photographs in the ED). As long as the amputation is distal to the distal interphalangeal crease the result should be very good.
Pulp / fingertip incisions
- Linear lacerations should be cleaned and closed with 5.0 or 6.0 novafil.
- If left mal-aligned permanent sensory and functional loss may result
- Remember that even with elevation in a broad arm sling, fingertip injuries often swell so do not over tighten your sutures.
- Local GP should be requested for ROS in 5 -7 days.
Analgesia
- Marcaine [BestBets] ring block. Test digital nerves before injecting!
Hand lacerations
- Simple, uncomplicated hand lacerations do not require prophylactic antibiotics[BestBets]
subungual haematoma
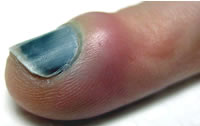
- Crush injury
- X-ray for # if significant force / pain
- Trephine & drain haematoma if > 25% nail
- Nail removal not indicated [BestBets]
- Non adherent dressing
- GP follow up
- No antibiotics for uncomplicated subungual haematoma[BestBets]
- Antibiotics if # and wound open / intervention [BestBets]
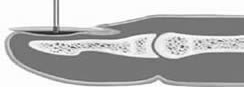
Paronychia / Felon#
Acute paronychia develops over a few hours when a nail fold becomes painful, red and swollen.
Throbbing pain indicated presence of pus
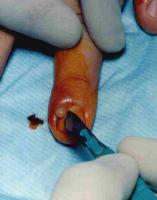 Usually staphylococcus
Usually staphylococcus- F : M = 3:1
- Ask about background Diabetes, Immunosuppression, Raynaud's or fungal infections
- Acute case treat with incision / elevation nail fold (image right) rather than antibiotics[BestBets]
- Recurrent paronychia or if nail bed involvement best treated by removing whole nail
Paronychia DDx includes
- Felon
- Herpetic whitlow
- (right)Malignant tumours
- Fungal infection
- Pemphigus vulgaris
- Splinters, foreign body
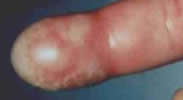
Felon
- Deeper pulp space infection
- Risk of osteomyelitis of distal phalanx
- Treat with I&D - longitudinal incision parallel with nail
Hand injury referrals:
Severe hand injuries have very long-term implications for patients. Efficient management and referral are of paramount importance. In this EM service the following referral protocol should be followed:
Referral CUH fracture clinic:
- Major hand injuries, including compound fractures / joint injuries, digital nerve division, tendon injuries Referral form
- Discuss emergency management with the Orthopaedic Registrar on-call who will also advise time and location of referral
You MUST discuss the case with the your Duty Doc before discussing with the plastics team.